Timer Handler(定时器处理程序)
显示原文
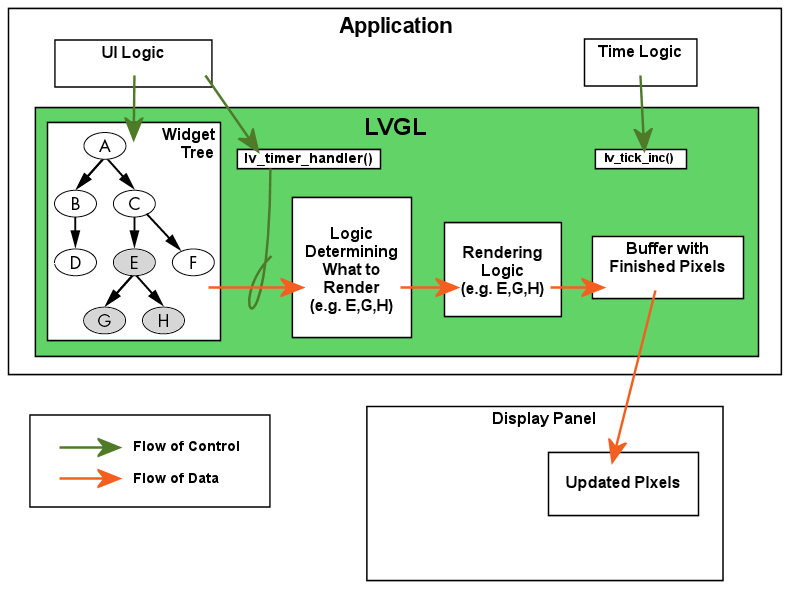
To drive the timers of LVGL you need to call lv_timer_handler()
periodically in one of the following:
while(1) of main() function, or
an OS task periodically. (See LVGL and Threads(LVGL 与线程).)
Example:
while(1) {
uint32_t time_till_next = lv_timer_handler();
my_delay_ms(time_till_next);
}
If you want to use lv_timer_handler() in a super-loop, a helper
function lv_timer_handler_run_in_period() is provided to simplify
supplying LVGL with time awareness:
while(1) {
...
lv_timer_handler_run_in_period(5); /* run lv_timer_handler() every 5ms */
...
}
Or use the sleep time automatically calculated by LVGL:
while(1) {
...
lv_timer_periodic_handler();
...
}
In an OS environment, you can use it together with the delay or sleep provided by OS to release CPU whenever possible:
while (1) {
uint32_t time_till_next = lv_timer_handler();
os_delay_ms(time_till_next); /* delay to avoid unnecessary polling */
}
See Timers(定时器) section to learn more about timers. .. raw:: html
</details> <br>
要驱动 LVGL 的定时器,需要在以下情况之一中定期调用 lv_timer_handler() 函数:
- 在 main() 函数的 while(1) 循环中,或者
- 在操作系统任务中定期调用。(请参阅 LVGL and Threads(LVGL 与线程) 。)
示例:
while(1) {
uint32_t time_till_next = lv_timer_handler();
my_delay_ms(time_till_next);
}
如果想在主循环中使用 lv_timer_handler() ,提供了一个辅助函数 lv_timer_handler_run_in_period() 来简化为 LVGL 提供时间感知的操作:
while(1) {
...
lv_timer_handler_run_in_period(5); /* run lv_timer_handler() every 5ms */
...
}
或者使用由 LVGL 自动计算出的休眠时间:
while(1) {
...
lv_timer_periodic_handler();
...
}
在操作系统环境中,可以将它与操作系统提供的 延迟 或 休眠 功能一起使用,以便在可能的情况下释放 CPU 资源:
while (1) {
uint32_t time_till_next = lv_timer_handler();
os_delay_ms(time_till_next); /* delay to avoid unnecessary polling */
}
要了解更多关于定时器的内容,请参阅 Timers(定时器) 部分。 API *** .. Autogenerated